Climate Change
Your Toronto Zoo’s vision is a world where people, wildlife, and wild spaces thrive. We are all interconnected, and we must take steps to safeguard our shared global ecosystem from the impacts of climate change.
what is climate change?
When you hear the term “climate change,” many different ideas and definitions may come to mind. But did you know there’s a difference between short-term weather fluctuations and long-term shifts in our climate?
Understanding these distinctions is key to making sense of climate science and the challenges we face in addressing climate change.
- Climate (or climate change): refers to the long-term or average (30-50 year) shifts in temperatures, precipitation and wind. While some changes to weather patterns and environmental conditions are natural and occur over thousands (or millions) of years, human activities have accelerated these changes at an unprecedented rate.
- Climate variability: The natural variation in climate that occurs over months to decades (for example, changes in oceanic circulation, such as an El Niño)
- Weather: individual atmospheric conditions that is part of the long-term patterns of a certain climate.
- Global Warming: The long-term increase in Earth's average surface temperature due to human activities, primarily the release of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere.
what causes climate change?
Climate change happens partly because carbon dioxide, made by humans, builds up in the atmosphere and traps heat. When we burn fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas, more carbon dioxide is released into the air, forming a heat-trapping layer around the Earth.
This layer works like a blanket, warming the air, land, and oceans. This change upsets the balance of the atmosphere that keeps our climate steady. As a result, climates that animals and plants need to survive are being affected.
 Industrial Processes: Factories and production releasing greenhouse gases.
Industrial Processes: Factories and production releasing greenhouse gases. Burning Fossil Fuels (Energy): Releasing primarily CO₂, the most prevalent greenhouse gas, and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
Burning Fossil Fuels (Energy): Releasing primarily CO₂, the most prevalent greenhouse gas, and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Deforestation: Increasing atmospheric CO₂ by cutting down trees that help absorb excess greenhouse gases.
Deforestation: Increasing atmospheric CO₂ by cutting down trees that help absorb excess greenhouse gases. Agriculture: Livestock producing methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
Agriculture: Livestock producing methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Transportation: Vehicles (including cars, trucks, airplanes and ships) use fossil fuels and when burned, they release CO₂
Transportation: Vehicles (including cars, trucks, airplanes and ships) use fossil fuels and when burned, they release CO₂ Urbanization
UrbanizationTypes of Greenhouse Gases (GHG)
While many gases contribute to the greenhouse effect, we often refer to carbon dioxide (CO₂) or its equivalent (CO₂e) when discussing climate change. This is because CO₂ is the most abundant and measurable greenhouse gas emitted from human activities, particularly through fossil fuel combustion. Additionally, although gases like methane (CH₄) and nitrous oxide (N₂O) occur in smaller amounts, they have a much higher global warming potential than CO₂. This means that molecule for molecule, they can trap significantly more heat, contributing to the greenhouse effect at levels comparable to CO₂. Expressing their impact as CO₂e allows us to combine and compare the warming effects of all greenhouse gases on a single, common scale, thereby simplifying the discussion and aiding in the development of effective mitigation strategies.
 Carbon Dioxide (CO₂)
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂)-
- The most significant human-caused greenhouse gas.
- Released through burning fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas), deforestation, and industrial processes.
- Can remain in the atmosphere for centuries.
 Methane (CH₄)
Methane (CH₄)-
- A more potent heat-trapping gas than CO₂ but has a shorter atmospheric lifespan.
- Emitted from livestock digestion, rice paddies, landfills, and natural gas leaks.
 Nitrous Oxide (N₂O)
Nitrous Oxide (N₂O)-
- Has a much greater heat-trapping ability than CO₂.
- Released from agricultural activities (fertilizers), fossil fuel combustion, and certain industrial processes.
 Water (h₂O)
Water (h₂O)-
- The most abundant greenhouse gas.
- Plays a natural role in trapping heat but is influenced by temperature changes rather than human activity.
Sources of Heat-Trapping Gas Emissions

While many gases contribute to the greenhouse effect, we often refer to carbon dioxide (CO₂) or its equivalent (CO₂e) when discussing climate change. This is because CO₂ is the most abundant and measurable greenhouse gas emitted from human activities, particularly fossil fuel combustion. Using CO₂e also allows us to express the combined warming potential of various greenhouse gases on a common scale, simplifying comparisons and informing effective mitigation strategies.
“We are losing species faster than ever, and we need communities to come together to fight species decline, climate change and biodiversity loss.”
why does it matter?
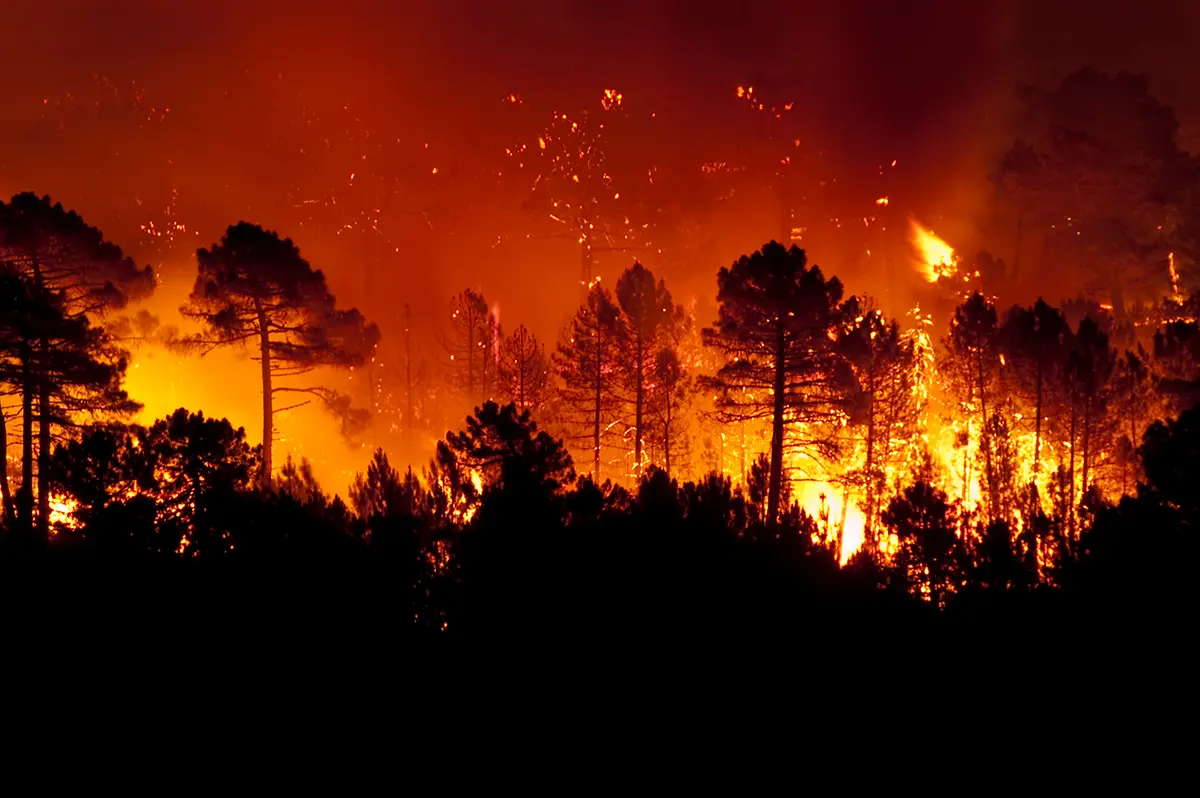
- Weather Events – Weather patterns are becoming less predictable, impacting communities and ecosystems around the world. Changes to the evaporation and precipitation cycle are causing more frequent and severe weather, such as heatwaves, hurricanes, droughts, floods, and wildfires. Globally, shifting seasons are disrupting the growth cycles of many organisms.
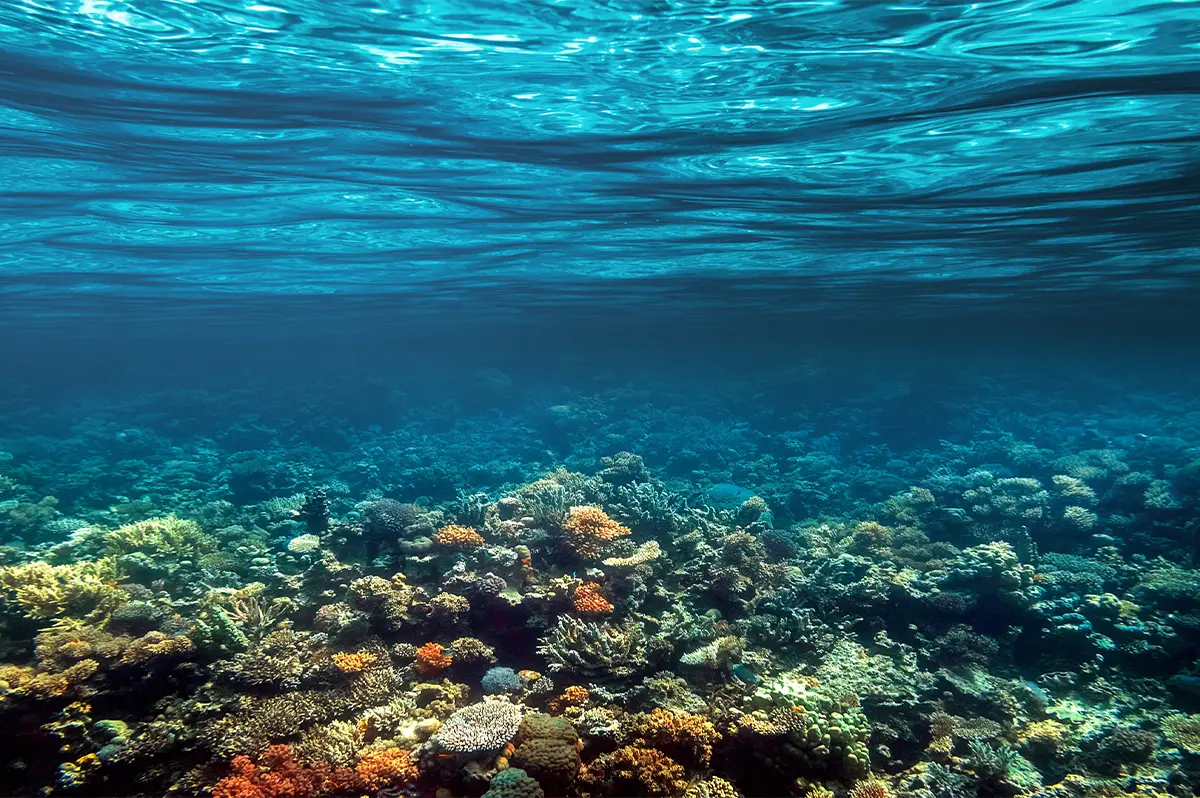
- Ocean Changes – Excess CO₂ isn’t confined to the atmosphere, about one-third is absorbed by the ocean. Acting as the climate’s heart, the ocean stores and redistributes heat through its currents, helping to moderate global temperatures. However, this CO₂ uptake alters the ocean’s chemistry, leading to acidification that weakens marine life like corals and shellfish (often referred to as "osteoporosis of the sea”).
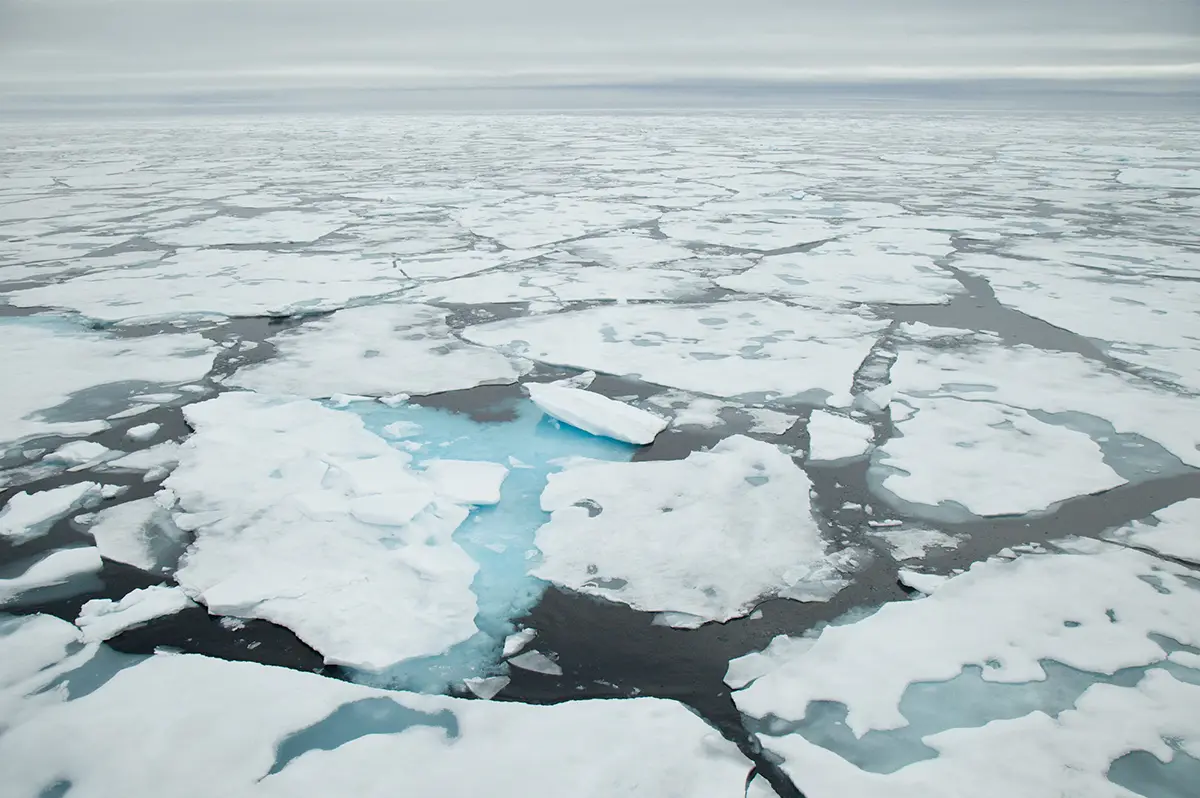
- Melting Ice and Rising Sea levels – The Arctic is warming four times faster than the rest of the planet, severely affecting organisms that rely on glaciers and sea ice for survival. The loss of Arctic sea ice not only threatens species, such as polar bears, but also contributes to rising sea levels, endangering coastal regions. Additionally, as ice melts, less sunlight is reflected back into space, leading to increased absorption of heat and further warming of the planet.
- Impacts on Ecosystems and Biodiversity – Climate change is accelerating biodiversity loss and placing new pressures on animal and plant populations. Habitats are shifting or disappearing, endangering plants and animals that are forced to migrate or face extinction.
- Invasive Species – Changes in temperature, rainfall, and elevated CO₂ levels make ecosystems more hospitable for invasive species allowing them to move into new areas where they could not survive before. This invasion disrupts food webs and alters ecosystems, permitting invasive species to outcompete native species for resources.
- Disease Spread – Rising global temperatures create environmental conditions that favour the growth and spread of pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi, leading to more frequent and severe disease outbreaks.
- Human Impacts – Climate change also impacts you. In addition to changes in weather patterns and extreme events, the impacts of climate change are affecting agriculture, water resources, health and economies.
“Future generations depend on the decisions we make today”
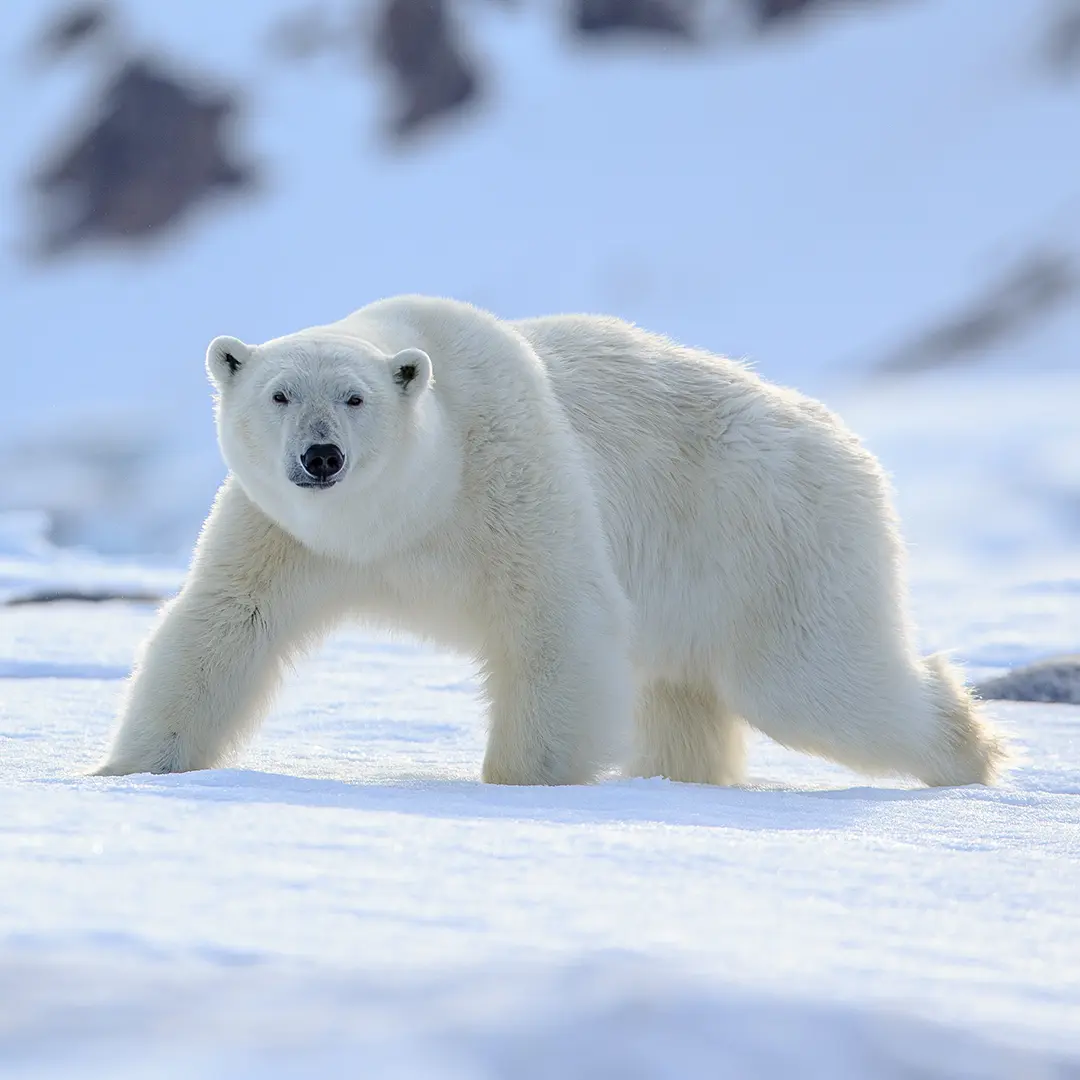

Polar bears (Vulnerable)

Red Pandas (Endangered)

Sumatran orangutans (Critically Endangered)

Western lowland gorillas (Critically Endangered)

Masai giraffe (Endangered)

Snow leopards (Vulnerable)

African penguins (Critically Endangered)

White Rhinos (Near Threatened)

Amur tigers (Endangered)

Frog populations

Turtle populations
what can we do about it?
“Together, we can reduce our fossil fuel usage and GHG emissions in order to help wildlife and their habitats for future generations to ensure healthy populations of animals, and people, too”
A Global Push for Climate Action
Across the world, individuals, communities, NGOs, governments, and industries are uniting in a powerful movement to mitigate climate change and secure a sustainable future for our planet. These collective efforts demonstrate that when we work together, we can protect our environment, preserve biodiversity, and ensure a healthy planet for animals and people alike.
-
Local and Individual Action:
Grassroots initiatives and local projects are making a significant impact. Whether it’s adopting eco-friendly habits at home, engaging in community renewable energy projects, or supporting local conservation efforts, individual actions contribute to a larger movement. Open conversations about sustainable practices encourage community involvement and foster innovative solutions. -
NGO and Community Initiatives:
Non-governmental organizations play a pivotal role in raising awareness, educating the public, and driving tangible environmental improvements. NGOs are leading campaigns, organizing community-based projects, and partnering with local groups to implement sustainable practices that reduce emissions and protect natural habitats. -
Government Initiatives:
Governments around the world are stepping up to address climate change through comprehensive policies and international agreements like the Paris Agreement. National and local governments are investing in renewable energy infrastructure, enforcing regulations that lower greenhouse gas emissions, and implementing measures such as carbon pricing and energy efficiency standards. These actions create a robust framework for sustainable development and environmental protection. -
Industry Leadership:
Industries are increasingly embracing sustainability by investing in cleaner technologies and transforming their operations. Companies across sectors, from automotive and energy to manufacturing, are adopting renewable energy sources, reducing waste, and developing innovative solutions to lower their environmental footprint. By setting ambitious sustainability targets and collaborating on green initiatives, the private sector is playing a key role in driving global climate action.
Through coordinated action at every level—local, national, and international—we are making strides in reducing emissions, protecting vital ecosystems, and ensuring a vibrant future. The collaborative efforts of individuals, communities, NGOs, governments, and industries provide hope and clear evidence that all is not lost. Together, we can safeguard our planet, protect its diverse species, and build a resilient world for generations to come.
- Let’s Talk! By starting to talk about climate change (and solutions) with your friends, family and peers, this open dialogue increases understanding, awareness and opportunity for the collective to spark change.
- VOTE with the climate in mind! The most impactful way you can make a difference is to vote with the climate in mind. Cast your ballot in the next election with wildlife in mind and let your local representative know you support bold climate action.
- Support an Energy Shift! Get involved with community projects that reduce or replace fossil fuels with clean energy sources like solar and wind, and research options that may be available to you at home.
- Build A Better Future! Encourage and support energy-efficient construction standards that include more efficient heating and cooling systems, insulation and lighting methods.
- Promote Clean Transportation! Support community initiatives that promote reducing individual vehicle traffic such as car sharing and public transit.
- Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle!
Embrace sustainable consumption by reducing waste and reusing items whenever possible. Choose products with minimal packaging and support businesses that prioritize eco-friendly practices. - Support Conservation and Reforestation!
Participate in or donate to local reforestation and conservation projects. Planting trees and preserving natural habitats help absorb carbon dioxide and support biodiversity.
Our Commitment
OUR SUSTAINABLITY VISION: WE ENVISION A ZOO WHOSE OPERATIONS PRODUCE AN OVERALL BENEFIT TO OUR NATURAL ENVIRONMENT, ALLOWING WILDLIFE AND WILD SPACES TO THRIVE
Today:

By connecting our Areas of Focus with Climate as one of our 4 Cares within our 2025-2027 Strategic Plan, we show how every action drives us forward. These aren’t just plans—they’re bold steps that challenge the status quo, push boundaries, and fuel our mission to protect wildlife and ignite meaningful change at Your Toronto Zoo.
BELONGING
Expand transit connections and options for team members and guests to access the Zoo site.
NATURE’S INSURANCE POLICY
Monitor wildlife disease risk and live/share best practices.Evaluate Zoo land management practices and the Plant Lives with Purpose plan to promote healthy ecosystems and animal food security.
WILDLIFE ADVOCATES
Establish partnerships with global organizations to accelerate conservation impact.Build community literacy on the role of synthetic biology in conservation and the potential risk of genetically modified wildlife.
WOW FOR GOOD
Embrace an innovation culture to build the most technologically advanced Zoo in the world.Act as a demonstration site for climate mitigation, waste management and renewable energy projects/practices.
Embrace the arts to improve guest experience and make new connections between climate change, biodiversity loss and communities.
tomorrow
Your Toronto Zoo has developed an ambitious TZNet0 Sustainability Plan that goes beyond the gates and prioritizes reducing its ecological footprint and contributing to global environmental efforts.
By setting aggressive goals to reduce our water consumption, GHG emissions and increase waste diversion, our goal is to be one of many organizations in our community and beyond that make these changes in the future to better our planet.
Through these aggressive and forward-looking initiatives, our goal is to enhance our environmental stewardship, being a key player in the global movement toward sustainability. Join us in this larger collective effort to make lasting changes in our communities and industries, thereby ensuring a healthier planet for future generations.
“We appreciate your commitment to individuals and healthy populations thriving and are grateful you share our vision of a world where people, wildlife and wild spaces thrive.”
Toronto Zoo | Strat Plan
We are thankful for the shared commitment of our incredible partners working to address the climate crisis alongside us.