Siamese catfish
Pangasius sutchi
Order: Siluriformes
Family: Pangasiidae
Genus: Pangasius
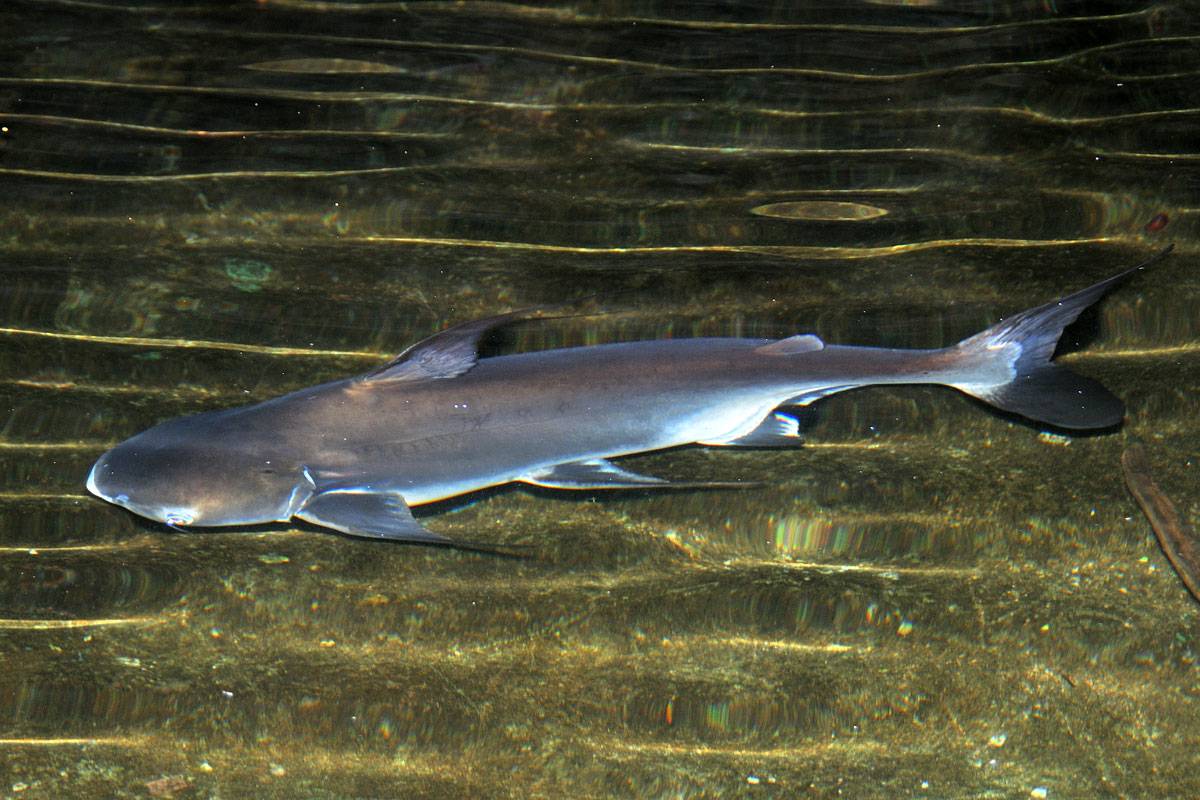
Length up to 100 cm or more. The elongated dark grey body resembles that of a shark. It has large eyes, a small mouth and the tail is deeply forked. The back is darker than the main body colour. A slender, horizontal, white stripe extends from the base of the tail to the gill cover. The fins are light grey to transparent. Males are more slender and have darker striping than the females.
Conservation Status: IUCN
Distribution
Southeast Asia, particularly Mekong and Maeklong basins, but has been introduced elsewhere.
Habitat
Tropical freshwater: found in large schools, swimming in rapid areas of large rivers.
Diet
Omnivorous, feeding on smaller fishes and crustaceans as well as vegetable debris.
Reproduction
It moves upstream to spawn during the flood season while the waters are high and returns downstream to seek rearing habitats when the water levels recede. The dates of the migrations vary depending on the river system. In the Mekong river basin, they migrate upstream in May to July and return downstream during September through December. South of the Khone Falls, upstream migration occurs in October to February, with its peak in November to December. The habitat consists of rapids and sandbanks, interspersed with deep rocky channels and pools. Spawning takes place during the monsoon season. Large numbers of eggs are laid. Egg production increases dramatically with the size of the fish. Larvae and fry drift downstream with the current.
Adaptation
It can survive under varied water conditions. It consumes anything edible. It is migratory moving with flood waters, utilizing floodplains.
Threats to Survival
In its original habitat, the Mekong Delta, it was extensively fished. It is an important aquaculture food fish and has been introduced and farmed throughout Southeast Asia. Siamese catfish that escape from aquaculture facilities may compete with wild fish and have habitat and environmental impacts, especially in areas where Siamese catfish are not yet established.